Documentation
¶
Documentation
¶
Overview ¶
Package atreugo is a high performance and extensible micro web framework with zero memory allocations in hot paths
It's build on top of fasthttp and provides the following features:
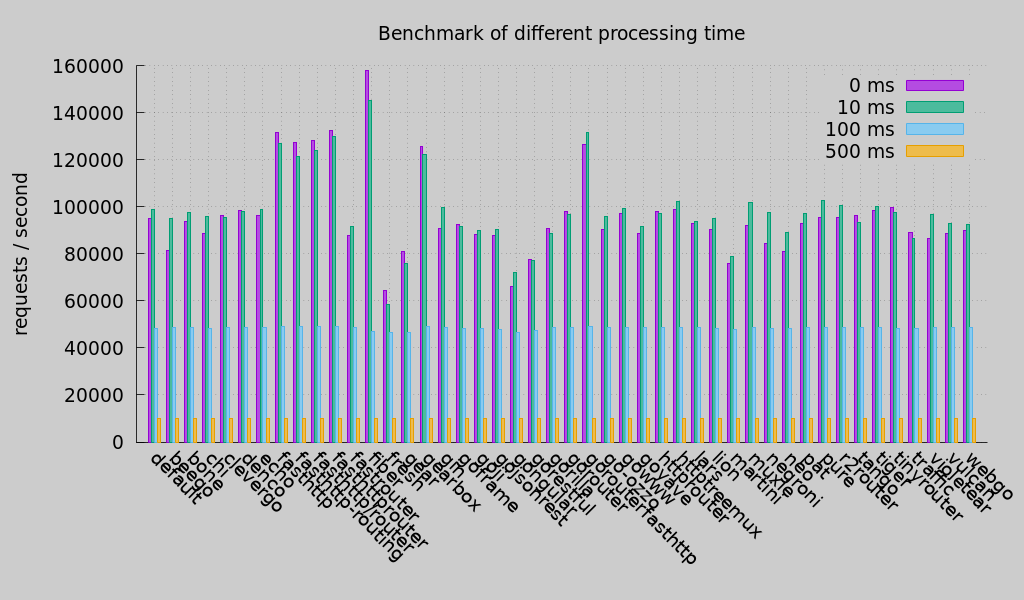
Optimized for speed. Easily handles more than 100K qps and more than 1M concurrent keep-alive connections on modern hardware.
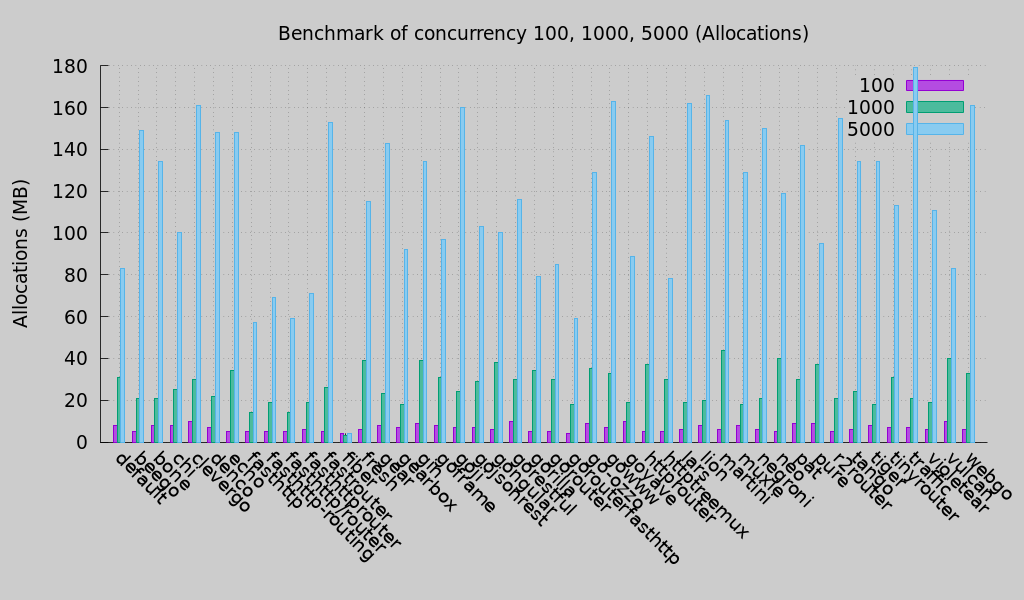
Optimized for low memory usage.
Easy 'Connection: Upgrade' support via RequestCtx.Hijack.
Server provides the following anti-DoS limits:
The number of concurrent connections.
The number of concurrent connections per client IP.
The number of requests per connection.
Request read timeout.
Response write timeout.
Maximum request header size.
Maximum request body size.
Maximum request execution time.
Maximum keep-alive connection lifetime.
Early filtering out non-GET requests.
* A lot of additional useful info is exposed to request handler:
- Server and client address.
- Per-request logger.
- Unique request id.
- Request start time.
- Connection start time.
- Request sequence number for the current connection.
* Middlewares support:
- Before view execution.
- After view execution.
* Easy routing:
- Path parameters (mandatories and optionals).
- Views with timeout.
- Group paths and middlewares.
- Static files.
- Serve one file like pdf, etc.
- Middlewares for specific views.
- fasthttp handlers support
- net/http handlers support.
* Common responses (also you could use your own responses):
- JSON
- HTTP
- Text
- Raw
- File
- Redirect
Index ¶
- Constants
- func IsPreforkChild() bool
- func ReleaseRequestCtx(ctx *RequestCtx)
- type Atreugo
- func (s *Atreugo) HandleMethodNotAllowed(v bool)
- func (s *Atreugo) HandleOPTIONS(v bool)
- func (s *Atreugo) ListenAndServe() error
- func (s *Atreugo) NewVirtualHost(hostnames ...string) *Router
- func (s *Atreugo) RedirectFixedPath(v bool)
- func (s *Atreugo) RedirectTrailingSlash(v bool)
- func (s *Atreugo) SaveMatchedRoutePath(v bool)
- func (s *Atreugo) Serve(ln net.Listener) error
- func (s *Atreugo) ServeConn(c net.Conn) error
- func (s *Atreugo) ServeGracefully(ln net.Listener) error
- type Config
- type ErrorView
- type FinalMiddleware
- type JSON
- type Logger
- type Middleware
- type Middlewares
- type PanicView
- type Path
- func (p *Path) Middlewares(middlewares Middlewares) *Path
- func (p *Path) SkipMiddlewares(fns ...Middleware) *Path
- func (p *Path) Timeout(timeout time.Duration, msg string) *Path
- func (p *Path) TimeoutCode(timeout time.Duration, msg string, statusCode int) *Path
- func (p *Path) UseAfter(fns ...Middleware) *Path
- func (p *Path) UseBefore(fns ...Middleware) *Path
- func (p *Path) UseFinal(fns ...FinalMiddleware) *Path
- type PathRewriteFunc
- type RequestCtx
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) AttachContext(extraCtx context.Context)
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) AttachedContext() context.Context
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) ErrorResponse(err error, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) FileResponse(fileName, filePath, mimeType string) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) HTTPResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) HTTPResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) JSONResponse(body interface{}, statusCode ...int) (err error)
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) MatchedRoutePath() []byte
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) Next() error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) RawResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) RawResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) RedirectResponse(url string, statusCode int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) RequestID() []byte
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) SkipView()
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) TextResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) TextResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
- func (ctx *RequestCtx) Value(key interface{}) interface{}
- type Router
- func (r *Router) ANY(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) DELETE(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) GET(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) HEAD(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) ListPaths() map[string][]string
- func (r *Router) Middlewares(middlewares Middlewares) *Router
- func (r *Router) NetHTTPPath(method, url string, handler http.Handler) *Path
- func (r *Router) NewGroupPath(path string) *Router
- func (r *Router) OPTIONS(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) PATCH(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) POST(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) PUT(url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) Path(method, url string, viewFn View) *Path
- func (r *Router) RequestHandlerPath(method, url string, handler fasthttp.RequestHandler) *Path
- func (r *Router) ServeFile(url, filePath string) *Path
- func (r *Router) SkipMiddlewares(fns ...Middleware) *Router
- func (r *Router) Static(url, rootPath string) *Path
- func (r *Router) StaticCustom(url string, fs *StaticFS) *Path
- func (r *Router) UseAfter(fns ...Middleware) *Router
- func (r *Router) UseBefore(fns ...Middleware) *Router
- func (r *Router) UseFinal(fns ...FinalMiddleware) *Router
- type StaticFS
- type View
Constants ¶
const XRequestIDHeader = "X-Request-ID"
XRequestIDHeader header name of request id.
Variables ¶
This section is empty.
Functions ¶
func IsPreforkChild ¶ added in v11.2.0
func IsPreforkChild() bool
IsPreforkChild checks if the current thread/process is a child.
func ReleaseRequestCtx ¶ added in v11.2.0
func ReleaseRequestCtx(ctx *RequestCtx)
ReleaseRequestCtx returns ctx acquired via AcquireRequestCtx to request context pool.
It is forbidden accessing ctx and/or its' members after returning it to request pool.
Types ¶
type Atreugo ¶
type Atreugo struct {
*Router
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Atreugo implements high performance HTTP server
It is prohibited copying Atreugo values. Create new values instead.
func (*Atreugo) HandleMethodNotAllowed ¶
HandleMethodNotAllowed if enabled, the router checks if another method is allowed for the current route, if the current request can not be routed. If this is the case, the request is answered with 'Method Not Allowed' and HTTP status code 405. If no other Method is allowed, the request is delegated to the NotFound handler.
It's activated by default.
func (*Atreugo) HandleOPTIONS ¶
HandleOPTIONS if enabled, the router automatically replies to OPTIONS requests. Custom OPTIONS handlers take priority over automatic replies.
It's activated by default.
func (*Atreugo) ListenAndServe ¶
ListenAndServe serves requests from the given network and address in the atreugo configuration.
Pass custom listener to Serve/ServeGracefully if you want to use it.
func (*Atreugo) NewVirtualHost ¶ added in v11.4.0
NewVirtualHost returns a new sub-router for running more than one web site (such as company1.example.com and company2.example.com) on a single atreugo instance. Virtual hosts can be "IP-based", meaning that you have a different IP address for every web site, or "name-based", meaning that you have multiple names running on each IP address.
The fact that they are running on the same atreugo instance is not apparent to the end user.
If you pass multiples hostnames, all of them will have the same behaviour.
func (*Atreugo) RedirectFixedPath ¶
RedirectFixedPath if enabled, the router tries to fix the current request path, if no handle is registered for it. First superfluous path elements like ../ or // are removed. Afterwards the router does a case-insensitive lookup of the cleaned path. If a handle can be found for this route, the router makes a redirection to the corrected path with status code 301 for GET requests and 307 for all other request methods. For example /FOO and /..//Foo could be redirected to /foo. RedirectTrailingSlash is independent of this option.
It's activated by default.
func (*Atreugo) RedirectTrailingSlash ¶
RedirectTrailingSlash enables/disables automatic redirection if the current route can't be matched but a handler for the path with (without) the trailing slash exists. For example if /foo/ is requested but a route only exists for /foo, the client is redirected to /foo with http status code 301 for GET requests and 307 for all other request methods.
It's activated by default.
func (*Atreugo) SaveMatchedRoutePath ¶
SaveMatchedRoutePath if enabled, adds the matched route path onto the ctx.UserValue context before invoking the handler. The matched route path is only added to handlers of routes that were registered when this option was enabled.
It's deactivated by default.
func (*Atreugo) Serve ¶
Serve serves incoming connections from the given listener.
Serve blocks until the given listener returns permanent error.
func (*Atreugo) ServeConn ¶ added in v11.2.4
ServeConn serves HTTP requests from the given connection.
ServeConn returns nil if all requests from the c are successfully served. It returns non-nil error otherwise.
Connection c must immediately propagate all the data passed to Write() to the client. Otherwise requests' processing may hang.
ServeConn closes c before returning.
type Config ¶
type Config struct {
Addr string
// TLS/SSL options
TLSEnable bool
CertKey string
CertFile string
// TLSConfig optionally provides a TLS configuration for use
// by Serve when TLSEnable is true.
//
// Note that this value is cloned by Serve,
// so it's not possible to modify the configuration
// with methods like tls.Config.SetSessionTicketKeys.
// To use SetSessionTicketKeys, use Atreugo.Serve with a TLS Listener
// instead.
TLSConfig *tls.Config
// Server name for sending in response headers. (default: Atreugo)
Name string
// Logger (optional)
Logger Logger
// Log debug traces
// Disabled by default
//
// Deprecated: Will be remove it soon!
Debug bool
// Kind of network listener (default: tcp4)
// The network must be "tcp", "tcp4", "tcp6" or "unix".
Network string
// Preforks master process (with all cores) between several child processes
// increases performance significantly, because Go doesn't have to share
// and manage memory between cores
//
// WARNING: using prefork prevents the use of any global state!
// Things like in-memory caches won't work.
//
// WARNING: In Windows OS it's only supported when 'Reuseport' is enabled.
Prefork bool
// Run server with a TCP listener with SO_REUSEPORT option set.
// Just supported tcp4 and tcp6.
//
// It is recommended to scale linearly, executing several instances (as many as usable logical CPUs)
// of the same server in different processes, significantly increasing performance.
//
// IMPORTANT: If you use it without prefork,
// each of these processes should be executed with GOMAXPROCS=1.
//
// See: https://www.nginx.com/blog/socket-sharding-nginx-release-1-9-1/.
Reuseport bool
// Shutdown gracefully shuts down the server without interrupting any active connections.
// Shutdown works by first closing all open listeners and then waiting indefinitely for all connections
// to return to idle and then shut down.
//
// WARNING: Windows is not supportted.
GracefulShutdown bool
// Signals from operating system to listen when GracefulShutdown is enabled.
//
// Default: SIGINT, SIGTERM
GracefulShutdownSignals []os.Signal
// Compress transparently the response body generated by handler if the request contains 'gzip' or 'deflate'
// in 'Accept-Encoding' header.
Compress bool
// Configurable view which is called when no matching route is
// found. If it is not set, http.NotFound is used.
NotFoundView View
// Configurable view which is called when a request
// cannot be routed.
// If it is not set, http.Error with http.StatusMethodNotAllowed is used.
// The "Allow" header with allowed request methods is set before the handler
// is called.
MethodNotAllowedView View
// Function to handle error returned by view.
// It should be used to generate a error page and return the http error code
// 500 (Internal Server Error).
ErrorView ErrorView
// Function to handle panics recovered from views.
// It should be used to generate a error page and return the http error code
// 500 (Internal Server Error).
// The handler can be used to keep your server from crashing because of
// unrecovered panics.
PanicView PanicView
// HeaderReceived is called after receiving the header
//
// non zero RequestConfig field values will overwrite the default configs
HeaderReceived func(header *fasthttp.RequestHeader) fasthttp.RequestConfig
// ContinueHandler is called after receiving the Expect 100 Continue Header
//
// https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec8.html#sec8.2.3
// https://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec10.html#sec10.1.1
// Using ContinueHandler a server can make decisioning on whether or not
// to read a potentially large request body based on the headers
//
// The default is to automatically read request bodies of Expect 100 Continue requests
// like they are normal requests
ContinueHandler func(header *fasthttp.RequestHeader) bool
// The maximum number of concurrent connections the server may serve.
//
// DefaultConcurrency is used if not set.
Concurrency int
// Per-connection buffer size for requests' reading.
// This also limits the maximum header size.
//
// Increase this buffer if your clients send multi-KB RequestURIs
// and/or multi-KB headers (for example, BIG cookies).
//
// Default buffer size is used if not set.
ReadBufferSize int
// Per-connection buffer size for responses' writing.
//
// Default buffer size is used if not set.
WriteBufferSize int
// ReadTimeout is the amount of time allowed to read
// the full request including body. The connection's read
// deadline is reset when the connection opens, or for
// keep-alive connections after the first byte has been read.
//
// By default request read timeout is unlimited.
ReadTimeout time.Duration
// WriteTimeout is the maximum duration before timing out
// writes of the response. It is reset after the request handler
// has returned.
//
// By default response write timeout is unlimited.
WriteTimeout time.Duration
// IdleTimeout is the maximum amount of time to wait for the
// next request when keep-alive is enabled. If IdleTimeout
// is zero, the value of ReadTimeout is used.
IdleTimeout time.Duration
// Maximum number of concurrent client connections allowed per IP.
//
// By default unlimited number of concurrent connections
// may be established to the server from a single IP address.
MaxConnsPerIP int
// Maximum number of requests served per connection.
//
// The server closes connection after the last request.
// 'Connection: close' header is added to the last response.
//
// By default unlimited number of requests may be served per connection.
MaxRequestsPerConn int
// MaxKeepaliveDuration is a no-op and only left here for backwards compatibility.
// Deprecated: Use IdleTimeout instead.
MaxKeepaliveDuration time.Duration
// MaxIdleWorkerDuration is the maximum idle time of a single worker in the underlying
// worker pool of the Server. Idle workers beyond this time will be cleared.
MaxIdleWorkerDuration time.Duration
// Period between tcp keep-alive messages.
//
// TCP keep-alive period is determined by operation system by default.
TCPKeepalivePeriod time.Duration
// Maximum request body size.
//
// The server rejects requests with bodies exceeding this limit.
//
// Request body size is limited by DefaultMaxRequestBodySize by default.
MaxRequestBodySize int
// Whether to disable keep-alive connections.
//
// The server will close all the incoming connections after sending
// the first response to client if this option is set to true.
//
// By default keep-alive connections are enabled.
DisableKeepalive bool
// Whether to enable tcp keep-alive connections.
//
// Whether the operating system should send tcp keep-alive messages on the tcp connection.
//
// By default tcp keep-alive connections are disabled.
TCPKeepalive bool
// Aggressively reduces memory usage at the cost of higher CPU usage
// if set to true.
//
// Try enabling this option only if the server consumes too much memory
// serving mostly idle keep-alive connections. This may reduce memory
// usage by more than 50%.
//
// Aggressive memory usage reduction is disabled by default.
ReduceMemoryUsage bool
// Rejects all non-GET requests if set to true.
//
// This option is useful as anti-DoS protection for servers
// accepting only GET requests. The request size is limited
// by ReadBufferSize if GetOnly is set.
//
// Server accepts all the requests by default.
GetOnly bool
// Will not pre parse Multipart Form data if set to true.
//
// This option is useful for servers that desire to treat
// multipart form data as a binary blob, or choose when to parse the data.
//
// Server pre parses multipart form data by default.
DisablePreParseMultipartForm bool
// Logs all errors, including the most frequent
// 'connection reset by peer', 'broken pipe' and 'connection timeout'
// errors. Such errors are common in production serving real-world
// clients.
//
// By default the most frequent errors such as
// 'connection reset by peer', 'broken pipe' and 'connection timeout'
// are suppressed in order to limit output log traffic.
LogAllErrors bool
// Will not log potentially sensitive content in error logs
//
// This option is useful for servers that handle sensitive data
// in the request/response.
//
// Server logs all full errors by default.
SecureErrorLogMessage bool
// Header names are passed as-is without normalization
// if this option is set.
//
// Disabled header names' normalization may be useful only for proxying
// incoming requests to other servers expecting case-sensitive
// header names. See https://github.com/valyala/fasthttp/issues/57
// for details.
//
// By default request and response header names are normalized, i.e.
// The first letter and the first letters following dashes
// are uppercased, while all the other letters are lowercased.
// Examples:
//
// * HOST -> Host
// * content-type -> Content-Type
// * cONTENT-lenGTH -> Content-Length
DisableHeaderNamesNormalizing bool
// SleepWhenConcurrencyLimitsExceeded is a duration to be slept of if
// the concurrency limit in exceeded (default [when is 0]: don't sleep
// and accept new connections immediately).
SleepWhenConcurrencyLimitsExceeded time.Duration
// NoDefaultServerHeader, when set to true, causes the default Server header
// to be excluded from the Response.
//
// The default Server header value is the value of the Name field or an
// internal default value in its absence. With this option set to true,
// the only time a Server header will be sent is if a non-zero length
// value is explicitly provided during a request.
NoDefaultServerHeader bool
// NoDefaultDate, when set to true, causes the default Date
// header to be excluded from the Response.
//
// The default Date header value is the current date value. When
// set to true, the Date will not be present.
NoDefaultDate bool
// NoDefaultContentType, when set to true, causes the default Content-Type
// header to be excluded from the Response.
//
// The default Content-Type header value is the internal default value. When
// set to true, the Content-Type will not be present.
NoDefaultContentType bool
// KeepHijackedConns is an opt-in disable of connection
// close by fasthttp after connections' HijackHandler returns.
// This allows to save goroutines, e.g. when fasthttp used to upgrade
// http connections to WS and connection goes to another handler,
// which will close it when needed.
KeepHijackedConns bool
// CloseOnShutdown when true adds a `Connection: close` header when the server is shutting down.
CloseOnShutdown bool
// StreamRequestBody enables request body streaming,
// and calls the handler sooner when given body is
// larger then the current limit.
StreamRequestBody bool
// ConnState specifies an optional callback function that is
// called when a client connection changes state. See the
// ConnState type and associated constants for details.
ConnState func(net.Conn, fasthttp.ConnState)
// FormValueFunc, which is used by RequestCtx.FormValue and support for customising
// the behaviour of the RequestCtx.FormValue function.
//
// NetHttpFormValueFunc gives a FormValueFunc func implementation that is consistent with net/http.
FormValueFunc fasthttp.FormValueFunc
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Config configuration to run server
Default settings should satisfy the majority of Server users. Adjust Server settings only if you really understand the consequences.
type ErrorView ¶
type ErrorView func(*RequestCtx, error, int)
ErrorView must process error returned by view.
type FinalMiddleware ¶ added in v11.10.0
type FinalMiddleware func(*RequestCtx)
FinalMiddleware must process all incoming requests after the other middlewares/view.
type JSON ¶
type JSON map[string]interface{}
JSON is a map whose key is a string and whose value an interface.
type Logger ¶ added in v11.6.0
type Logger interface {
Print(v ...interface{})
Printf(format string, args ...interface{})
}
Logger is used for logging messages.
type Middleware ¶
type Middleware View
Middleware must process all incoming requests before/after defined views.
type Middlewares ¶
type Middlewares struct {
Before []Middleware
After []Middleware
Skip []Middleware
Final []FinalMiddleware
}
Middlewares is a collection of middlewares with the order of execution and which to skip.
type PanicView ¶
type PanicView func(*RequestCtx, interface{})
PanicView must process panics recovered from views, if it's defined in configuration.
type Path ¶
type Path struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Path configuration of the registered view
It is prohibited copying Path values.
func (*Path) Middlewares ¶
func (p *Path) Middlewares(middlewares Middlewares) *Path
Middlewares defines the middlewares (before, after and skip) in the order in which you want to execute them only for the view
WARNING: The previous middlewares configuration could be overridden.
func (*Path) SkipMiddlewares ¶
func (p *Path) SkipMiddlewares(fns ...Middleware) *Path
SkipMiddlewares registers the middlewares that you want to skip only when executing the view.
func (*Path) Timeout ¶
Timeout sets the timeout and the error message to the view, which returns StatusRequestTimeout error with the given msg to the client if view didn't return during the given duration.
The returned view may return StatusTooManyRequests error with the given msg to the client if there are more concurrent views are running at the moment than Server.Concurrency.
func (*Path) TimeoutCode ¶
TimeoutCode sets the timeout and the error message to the view, which returns an error with the given msg and status code to the client if view didn't return during the given duration.
The returned view may return StatusTooManyRequests error with the given msg to the client if there are more concurrent views are running at the moment than Server.Concurrency.
func (*Path) UseAfter ¶
func (p *Path) UseAfter(fns ...Middleware) *Path
UseAfter registers the middlewares in the order in which you want to execute them only after the execution of the view.
func (*Path) UseBefore ¶
func (p *Path) UseBefore(fns ...Middleware) *Path
UseBefore registers the middlewares in the order in which you want to execute them only before the execution of the view.
func (*Path) UseFinal ¶ added in v11.10.0
func (p *Path) UseFinal(fns ...FinalMiddleware) *Path
UseFinal registers the given middlewares to be executed in the order in which they are added, after the view or group has been executed. These middlewares will always be executed, even if a previous middleware or the view/group returned a response.
type PathRewriteFunc ¶
type PathRewriteFunc func(ctx *RequestCtx) []byte
PathRewriteFunc must return new request path based on arbitrary ctx info such as ctx.Path().
Path rewriter is used in StaticFS for translating the current request to the local filesystem path relative to StaticFS.Root.
The returned path must not contain '/../' substrings due to security reasons, since such paths may refer files outside StaticFS.Root.
The returned path may refer to ctx members. For example, ctx.Path().
type RequestCtx ¶
type RequestCtx struct {
*fasthttp.RequestCtx
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
RequestCtx context wrapper of fasthttp.RequestCtx to adds extra funtionality
It is prohibited copying RequestCtx values. Create new values instead.
View should avoid holding references to incoming RequestCtx and/or its' members after the return. If holding RequestCtx references after the return is unavoidable (for instance, ctx is passed to a separate goroutine and ctx lifetime cannot be controlled), then the View MUST call ctx.TimeoutError() before return.
It is unsafe modifying/reading RequestCtx instance from concurrently running goroutines. The only exception is TimeoutError*, which may be called while other goroutines accessing RequestCtx.
func AcquireRequestCtx ¶ added in v11.2.0
func AcquireRequestCtx(ctx *fasthttp.RequestCtx) *RequestCtx
AcquireRequestCtx returns an empty RequestCtx instance from request context pool.
The returned RequestCtx instance may be passed to ReleaseRequestCtx when it is no longer needed. This allows RequestCtx recycling, reduces GC pressure and usually improves performance.
func (*RequestCtx) AttachContext ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) AttachContext(extraCtx context.Context)
AttachContext attach a context.Context to the RequestCtx
WARNING: The extra context could not be itself.
func (*RequestCtx) AttachedContext ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) AttachedContext() context.Context
AttachedContext returns the attached context.Context if exist.
func (*RequestCtx) ErrorResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) ErrorResponse(err error, statusCode ...int) error
ErrorResponse returns an error response.
func (*RequestCtx) FileResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) FileResponse(fileName, filePath, mimeType string) error
FileResponse return a streaming response with file data.
func (*RequestCtx) HTTPResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) HTTPResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
HTTPResponse return response with body in html format.
func (*RequestCtx) HTTPResponseBytes ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) HTTPResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
HTTPResponseBytes return response with body in html format.
func (*RequestCtx) JSONResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) JSONResponse(body interface{}, statusCode ...int) (err error)
JSONResponse return response with body in json format.
func (*RequestCtx) MatchedRoutePath ¶ added in v11.7.0
func (ctx *RequestCtx) MatchedRoutePath() []byte
MatchedRoutePath returns the matched route path if Atreugo.SaveMatchedRoutePath() is enabled.
func (*RequestCtx) Next ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) Next() error
Next pass control to the next middleware/view function.
func (*RequestCtx) RawResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) RawResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
RawResponse returns response without encoding the body.
func (*RequestCtx) RawResponseBytes ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) RawResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
RawResponseBytes returns response without encoding the body.
func (*RequestCtx) RedirectResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) RedirectResponse(url string, statusCode int) error
RedirectResponse redirect request to an especific url.
func (*RequestCtx) RequestID ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) RequestID() []byte
RequestID returns the "X-Request-ID" header value.
func (*RequestCtx) SkipView ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) SkipView()
SkipView sets flag to skip view execution in the current request
Use it in before middlewares.
func (*RequestCtx) TextResponse ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) TextResponse(body string, statusCode ...int) error
TextResponse return response with body in text format.
func (*RequestCtx) TextResponseBytes ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) TextResponseBytes(body []byte, statusCode ...int) error
TextResponseBytes return response with body in text format.
func (*RequestCtx) Value ¶
func (ctx *RequestCtx) Value(key interface{}) interface{}
Value returns the value associated with attached context or this context for key, or nil if no value is associated with key. Successive calls to Value with the same key returns the same result.
WARNING: The provided key should not be of type string or any other built-in to avoid extra allocating when assigning to an interface{}, context keys often have concrete type struct{}. Alternatively, exported context key variables' static type should be a pointer or interface.
If the key is of type string, try to use:
ctx.SetUserValue("myKey", "myValue")
ctx.UserValue("myKey")
instead of:
ctx.AttachContext(context.WithValue(myCtx, "myKey", "myValue"))
ctx.Value("myKey")
to avoid extra allocation.
type Router ¶
type Router struct {
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
Router dispatchs requests to different views via configurable routes (paths)
It is prohibited copying Router values. Create new values instead.
func (*Router) ANY ¶ added in v11.1.0
ANY shortcut for router.Path("*", url, viewFn)
WARNING: Use only for routes where the request method is not important.
func (*Router) Middlewares ¶
func (r *Router) Middlewares(middlewares Middlewares) *Router
Middlewares defines the middlewares (before, after and skip) in the order in which you want to execute them for the view or group
WARNING: The previous middlewares configuration could be overridden.
func (*Router) NetHTTPPath ¶
NetHTTPPath wraps net/http handler to atreugo view and registers it to the given path and method.
While this function may be used for easy switching from net/http to fasthttp/atreugo, it has the following drawbacks comparing to using manually written fasthttp/atreugo, request handler:
- A lot of useful functionality provided by fasthttp/atreugo is missing from net/http handler.
- net/http -> fasthttp/atreugo handler conversion has some overhead, so the returned handler will be always slower than manually written fasthttp/atreugo handler.
So it is advisable using this function only for quick net/http -> fasthttp switching. Then manually convert net/http handlers to fasthttp handlers. according to https://github.com/valyala/fasthttp#switching-from-nethttp-to-fasthttp.
func (*Router) NewGroupPath ¶
NewGroupPath returns a new router to group paths.
func (*Router) Path ¶
Path registers a new view with the given path and method
This function is intended for bulk loading and to allow the usage of less frequently used, non-standardized or custom methods (e.g. for internal communication with a proxy).
func (*Router) RequestHandlerPath ¶
func (r *Router) RequestHandlerPath(method, url string, handler fasthttp.RequestHandler) *Path
RequestHandlerPath wraps fasthttp request handler to atreugo view and registers it to the given path and method.
func (*Router) ServeFile ¶
ServeFile returns HTTP response containing compressed file contents from the given path
HTTP response may contain uncompressed file contents in the following cases:
- Missing 'Accept-Encoding: gzip' request header.
- No write access to directory containing the file.
Directory contents is returned if path points to directory.
func (*Router) SkipMiddlewares ¶
func (r *Router) SkipMiddlewares(fns ...Middleware) *Router
SkipMiddlewares registers the middlewares that you want to skip when executing the view or group.
func (*Router) Static ¶
Static serves static files from the given file system root
Make sure your program has enough 'max open files' limit aka 'ulimit -n' if root folder contains many files.
func (*Router) StaticCustom ¶
StaticCustom serves static files from the given file system settings
Make sure your program has enough 'max open files' limit aka 'ulimit -n' if root folder contains many files.
func (*Router) UseAfter ¶
func (r *Router) UseAfter(fns ...Middleware) *Router
UseAfter registers the middlewares in the order in which you want to execute them after the execution of the view or group.
func (*Router) UseBefore ¶
func (r *Router) UseBefore(fns ...Middleware) *Router
UseBefore registers the middlewares in the order in which you want to execute them before the execution of the view or group.
func (*Router) UseFinal ¶ added in v11.10.0
func (r *Router) UseFinal(fns ...FinalMiddleware) *Router
UseFinal registers the given middlewares to be executed in the order in which they are added, after the view or group has been executed. These middlewares will always be executed, even if a previous middleware or the view/group returned a response.
type StaticFS ¶
type StaticFS struct {
// Path to the root directory to serve files from.
Root string
// AllowEmptyRoot controls what happens when Root is empty. When false (default) it will default to the
// current working directory. An empty root is mostly useful when you want to use absolute paths
// on windows that are on different filesystems. On linux setting your Root to "/" already allows you to use
// absolute paths on any filesystem.
AllowEmptyRoot bool
// List of index file names to try opening during directory access.
//
// For example:
//
// * index.html
// * index.htm
// * my-super-index.xml
//
// By default the list is empty.
IndexNames []string
// Index pages for directories without files matching IndexNames
// are automatically generated if set.
//
// Directory index generation may be quite slow for directories
// with many files (more than 1K), so it is discouraged enabling
// index pages' generation for such directories.
//
// By default index pages aren't generated.
GenerateIndexPages bool
// Transparently compresses responses if set to true.
//
// The server tries minimizing CPU usage by caching compressed files.
// It adds CompressedFileSuffix suffix to the original file name and
// tries saving the resulting compressed file under the new file name.
// So it is advisable to give the server write access to Root
// and to all inner folders in order to minimize CPU usage when serving
// compressed responses.
//
// Transparent compression is disabled by default.
Compress bool
// Uses brotli encoding and fallbacks to gzip in responses if set to true, uses gzip if set to false.
//
// This value has sense only if Compress is set.
//
// Brotli encoding is disabled by default.
CompressBrotli bool
// Path to the compressed root directory to serve files from. If this value
// is empty, Root is used.
CompressRoot string
// Enables byte range requests if set to true.
//
// Byte range requests are disabled by default.
AcceptByteRange bool
// Path rewriting function.
//
// By default request path is not modified.
PathRewrite PathRewriteFunc
// PathNotFound fires when file is not found in filesystem
// this functions tries to replace "Cannot open requested path"
// server response giving to the programmer the control of server flow.
//
// By default PathNotFound returns
// "Cannot open requested path"
PathNotFound View
// Expiration duration for inactive file handlers.
//
// FSHandlerCacheDuration is used by default.
CacheDuration time.Duration
// Suffix to add to the name of cached compressed file.
//
// This value has sense only if Compress is set.
//
// FSCompressedFileSuffix is used by default.
CompressedFileSuffix string
// Suffixes list to add to compressedFileSuffix depending on encoding
//
// This value has sense only if Compress is set.
//
// FSCompressedFileSuffixes is used by default.
CompressedFileSuffixes map[string]string
// If CleanStop is set, the channel can be closed to stop the cleanup handlers
// for the FS RequestHandlers created with NewRequestHandler.
// NEVER close this channel while the handler is still being used!
CleanStop chan struct{}
// contains filtered or unexported fields
}
StaticFS represents settings for serving static files from the local filesystem.
It is prohibited copying StaticFS values. Create new values instead.